|
Measure |




|
A Measure is a special Dimension that can be used to perform aggregate calculations. For example, a car dealership may have sales information on all cars sold, which would reside in information on each individual sale as exemplified below.
Date: March 1 Price: $25,000 Type: SUV
Date: March 20 Price: $32,000 Type: Sedan |
Date: April 5 Price: $15,000 Type: SUV
Date: April 9 Price: $22,000 Type: Sedan |
We can see that there are three Dimensions for each vehicle: Date, Price, and Type. An example of a Measure would be the Price dimension. The Price can be used to compute performance indicators, such as the average selling price for each vehicle type.
In addition, you should be aware that when creating Measures in the BI Architect, you will notice options for creating Formulas or using the Formula Button.
Here is a common example of Measure usage. In Figure 1, a table is inserted into a dashboard to display two columns of information. One column displays the dimension Country. For each country, we have now selected the sum function to calculate the sum of all retail sales for that country. This is the creation of a measure.
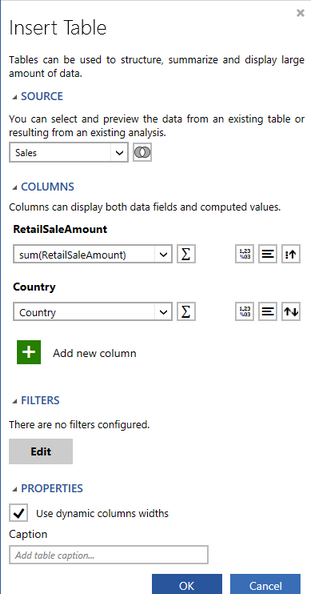
Figure 1: Using the sum function to create a measure.